Detailed explanation of PCR Technology
时间:2018-05-02 来源:EASTWIN浏览次数:79
Today, I would like to talk about the principles of polymerase chain reaction, the basic operation techniques of PCR, and the applications of PCR technology.
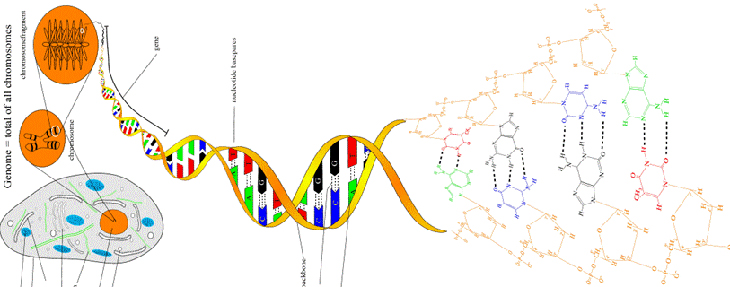
1 experiment principle
This technique can amplify a specific DNA fragment for millions of times in a test tube after several hours of reaction. This technique of rapid acquisition of a large number of single nucleic acids plays an important role in molecular biology, which greatly promotes the progress of life science. It is not only the most commonly used technology in DNA analysis, but also has important application value in DNA recombination and expression, gene structure analysis and function detection.
PCR can be regarded as a technique similar to the DNA replication process occurring within the cell, and the result is to produce a new complementary DNA fragment with the original DNA as a template. The replication of DNA in cells is a very complicated process. There are many factors involved in copying. PCR is a DNA replication reaction in test tube. The basic principle is similar to DNA replication in cells, but the reaction system is relatively simple.
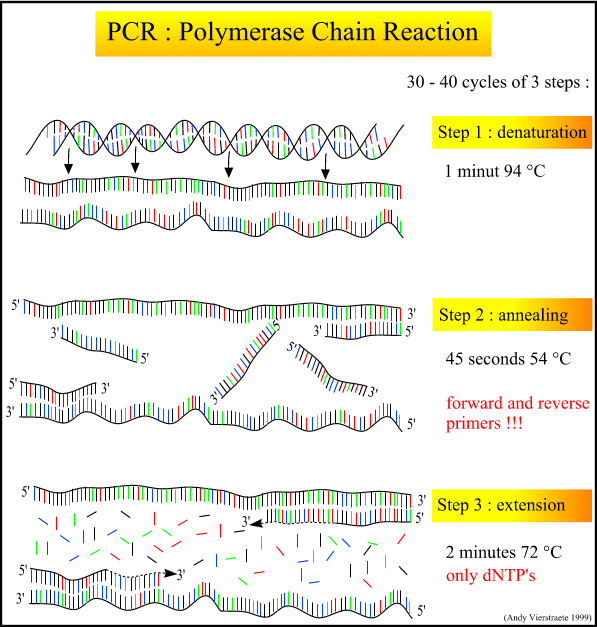
PCR consists of three basic reaction steps: denaturation annealing.
(1) the denaturation of the template DNA: the template DNA is heated to about 94 C for a certain time, and the double stranded DNA of the template DNA or PCR is dissociated to become a single chain, so that it is combined with the primers to prepare for the lower wheel reaction.
(2) annealing (refolding) of the template DNA and primers: after the template DNA was heated to a single strand by heating, the temperature dropped to about 55 degrees C, and the primers and the complementary sequence of the single strand of the template DNA were paired together.
(3) extension of primers: the DNA template primer conjugate, under the action of Taq enzyme, uses dNTP as the reaction material and the target sequence is a template. According to the principle of base pairing and semi preserved replication, a new semi retained copy chain complementing the template DNA chain is synthesized.
Repeated cyclic denaturation annealing -- extending the three process, can get more "half preserved replication chains" and this new chain can become a template for the next cycle. It takes 2~4 minutes to complete a cycle, and the amplification of the target gene can be magnified millions of times in 2~3 hours.
Template dna、2.5 mmol / l dntp
taq dna polymerase (5 u / μl) 、ssr primer
10 ×buffer、15 mmol / l mg2 + 、ddh₂o
PCR instrument、Pipette gun、pcr plate
3 Experimental steps
1. prepare the 20 L reaction system and add the following solutions in the PCR board:
|
Template DNA |
2 μL |
|
Primer 1 |
1 μL |
|
Primer 2 |
1 μL |
|
dNTP |
1.5 μL |
|
MgCl₂ |
2 μL |
|
10×buffer |
2 μL |
|
ddH₂O |
10 μL |
|
Taq enzyme |
0.5 μL |
2. set the PCR reaction program.
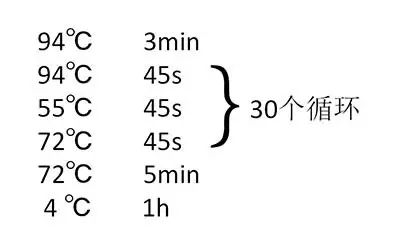
4. electrophoretic detection of the amplified products.
4 The technical application of PCR

1. Life Science
With the improvement of PCR, on the basis of the "work frame map" of the human genome completed in 2003, the scientists have been collated, classified and arranged to get a more accurate, clear and complete genome map. This is the first revelation of the basic appearance of the human genome, which indicates that scientists are beginning to "read" the contents of "the book of heaven" in human life.
B, post genome project
After the DNA sequence of the human genome is completed, the identification of genomic polymorphism and its haplotypes and the search for its application in biology and medicine have become a hot topic of concern. With the advent of the "post genome era" at the core of gene function, large-scale structural genome, proteome and drug genome project have become a new hot spot.
C, taxonomy, evolution and phylogenetic relationship of species
Conservatism analysis, species polymorphism analysis and species identification can be carried out for species evolution.
2. medicine
A, diagnosis and treatment of diseaseHereditary diseases, such as thalassemia, sickle cell anemia, and coagulation factor deficiency, are likely to be predicted, especially in the elderly, such as diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and even a part of the tumor; oncogene detection and diagnosis, detection of malignant tumor markers to diagnose cancer and other diseases; The use of gene therapy for the treatment of tumor disease.
Detection of B and pathogenic pathogens
The detection range includes bacteria, viruses (SARS, avian influenza virus H5N1, etc.), protozoa and parasites, molds, Rickettsia, chlamydia and mycoplasma. The sensitivity and specificity of the detection are far higher than the current immunological methods, and the time required has reached clinical requirements, which is especially suitable for the difficult to cultivate virus (hepatitis B), bacteria (such as tuberculosis, anaerobes) and protozoa (such as Treponema pallidum).
C, DNA fingerprint, individual identification (DNA identity card), parent-child relationship identification and forensic evidence.
It can be done with one hair, one cell and one sperm. This area has also been developed to match bone marrow or organ transplantation.
D, bioengineering pharmaceuticals
Many drugs can be produced in large quantities by engineering bacteria and cells, such as interferon, interleukin, erythropoietin and other drugs.
E, genetically modified animal pharmaceuticals and disease models
Transgenic animals are increasingly closely related to medical and biomedical research. In recent years, transgenic animal models of various human diseases have been established. Such as the application of transgenic animals in genetic disease, cardiovascular disease, tumor, hypertension, viral disease, xenotransplantation, transfusion medicine and pharmacology.
Using transgenic animal - mammary gland bioreactor to produce drug protein, it is like building a "pharmaceutical factory" on animal, and can continuously obtain stable bioactive gene products from animal milk. This is a completely new mode of drug production, which has the advantages of low investment cost, short drug development cycle and high economic benefits.
3. agricultural science
A, transgenic plantsAccording to its functions, it mainly improves yield, disease resistance, herbicide resistance, improved quality and developmental regulation. Such as soya bean, corn, potato, tomato and so on.
B, transgenic animals
In agriculture, it is mainly aimed at improving livestock and poultry production traits, improving disease resistance of livestock and poultry and producing unconventional livestock products using genetically modified livestock and poultry.
4. archeology and interpretation of historical events
Using human short tandem repeat STR-PCR technology to study the genetic polymorphism of human race, the effect is very stable. At present, this technology has been widely used in biological archaeology, phylogeny, ethnology, anthropology and archaeology.
5. health safety
A and detection of food microbesThe traditional detection of pathogenic bacteria is time-consuming and laborious after long time training. The application of PCR technology is very rapid and accurate. It is mainly used for the detection of food pathogenic bacteria, such as botulinum toxin, lactic acid bacteria and bacteria in water.
Detection of B and genetically modified foods
At present, there are more than 100 species of genetically modified foods in the world, most of which have been used for food. The harm of genetically modified food to human health and the impact on the ecology have also been widely paid attention in the world. Therefore, the detection of genetically modified foods has become a means to control the proliferation of genetically modified foods.
C, animal and plant quarantine
Sensitive, specific and rapid diagnostic testing methods are the gatekeepers of China's import and export ports, and whether people, animals, plants (livestock, seeds) and other pathogens, such as AIDS, animal viruses, plant viruses, etc., are checked for personnel, animals, plants, seeds, and so on, and whether food, feed or not with Salmonella and so on needs genetic diagnosis. To reject these pathogens outside the national boundaries is a necessary guarantee for improving our comprehensive national strength.
(Statement: content from the network, only for learning, sharing, copyright belongs to the original author, if inadvertently infringed your copyright, please send a letter to inform, this station will be deleted.)
- Previous:Common problems and answers to PCR instrument
- Next:Nothing To learn more Technical data>>>

 English
English 简体中文
简体中文




